File Allocation Methods - Contiguous
Of particular interest is the method that the basic file system uses to
place the logical file blocks onto the physical medium (for example, into
the disk's tracks and sectors on on spinning, magnetic HD).
 Contiguous File Allocation
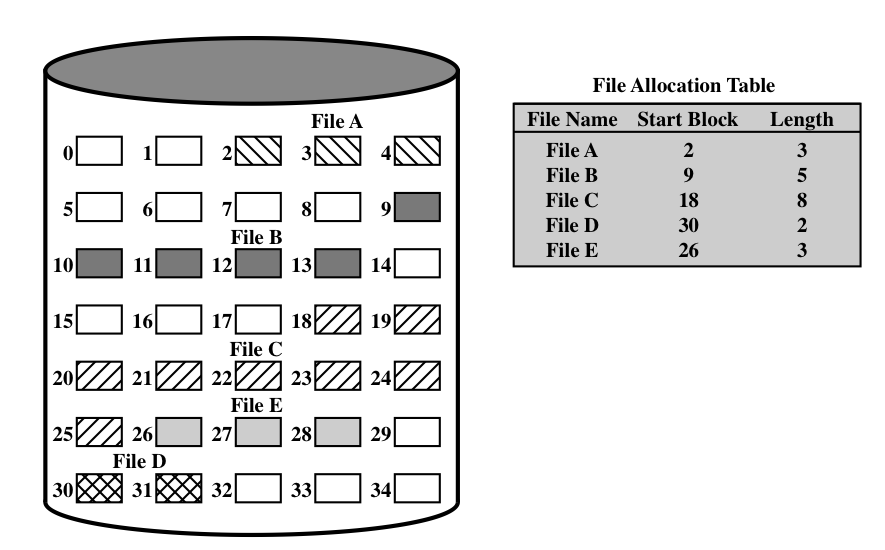
Contiguous File Allocation
The simplest policy (akin to memory partitioning in process management) is
the use of a fixed or contiguous allocation. This requires that a file's
maximum (ever) size be determined when the file is created, and that the
file cannot grow beyond this limit (as in the above figure).
The file allocation table stores,
for each file, its starting block and length.
Like simple memory allocation schemes, this method suffers from both
internal fragmentation (if the initial allocation is too large) and
external fragmentation (as files are deleted over time).
Again, as with memory allocation, a compaction scheme is required to reduce
fragmentation ("defragging" your disk).
CITS2002 Systems Programming, Lecture 15, p9, 18th September 2023.
|


 CITS2002
CITS2002 CITS2002 schedule
CITS2002 schedule