Initial Memory Allocation Using Partitioning, continued
Equal sized partitions introduce two problems:
- a process's requirements may exceed the partition size, and
- a small process still occupies a full partition. Such wastage of memory
is termed internal memory fragmentation.
The initial choice of partition -
the placement algorithm -
is, of course, trivial with equal-sized partitions.
Unequal sized partitions offer obvious advantages with respect to these
problems, but they complicate the placement algorithm. Either:
- a process is placed in the largest (large-enough) partition,
to minimise internal memory fragmentation, or
- a process is placed in the smallest (large-enough)
available partition.
The initial placement algorithm is again simple,
but also introduces excessive internal memory fragmentation.
|
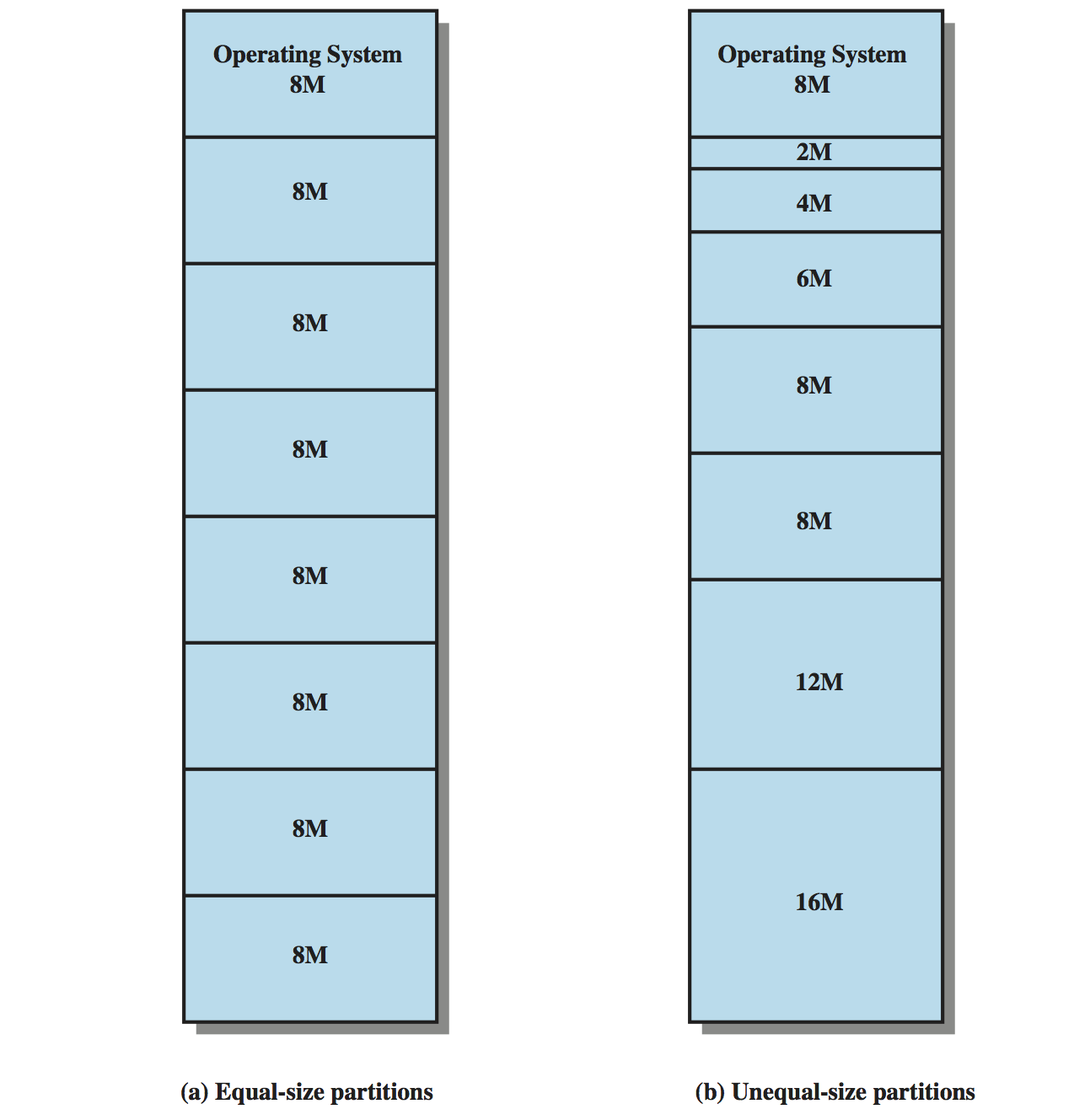 Example of Fixed Partitioning of a 64-Mbyte Memory
Example of Fixed Partitioning of a 64-Mbyte Memory
|
CITS2002 Systems Programming, Lecture 13, p5, 11th September 2023.
|


 CITS2002
CITS2002 CITS2002 schedule
CITS2002 schedule