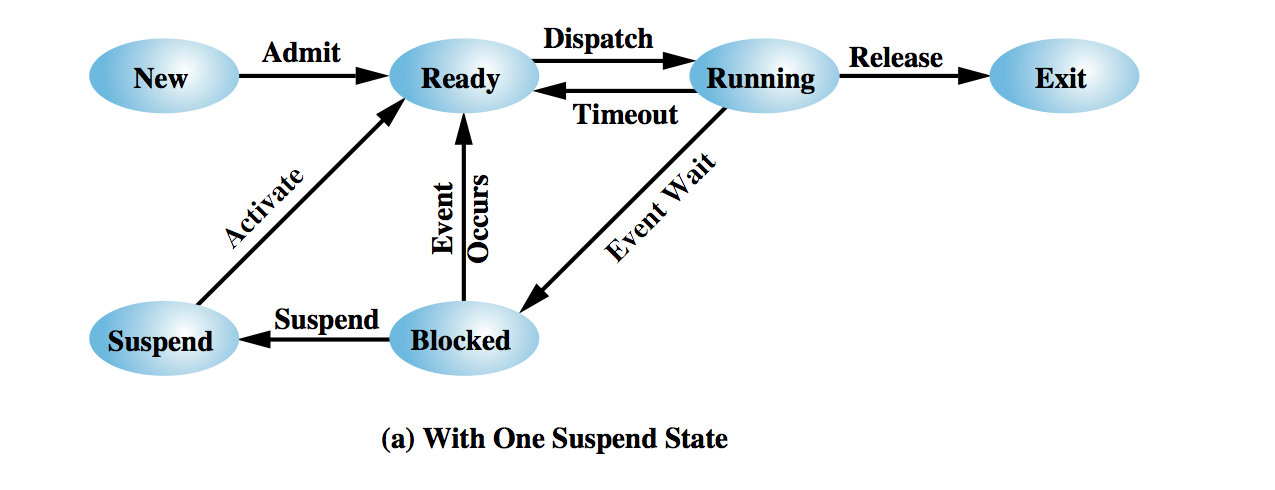
Suspension of Processes
Recall that the processor is much faster than I/O. As a consequence, it is
quite possible for all processes to be blocked on I/O requests, when the
processor will be idle most of the time while waiting for I/O interrupts.
Question: How to get more executing processes, given that resources such as
memory are finite?
To enable more true work to be performed by the processor, we could provide
more memory to support the requirements of more processes.
But aside from the expense, providing more memory tends to encourage larger
processes, not (in general) better support for more processes.
CITS2002 Systems Programming, Lecture 8, p13, 14th August 2024.
|


 CITS2002
CITS2002 CITS2002 schedule
CITS2002 schedule