

|
CITS3002 Computer Networks |
| ← prev | next → |  CITS3002
CITS3002 |
 help3002
help3002 |
 CITS3002 schedule
CITS3002 schedule |
|||
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)ARP is a low-level protocol that hides the underlying physical addressing, permitting one or more Internet addresses to be assigned to each machine. ARP is considered part of the physical network system, not strictly part of the Internet protocols.
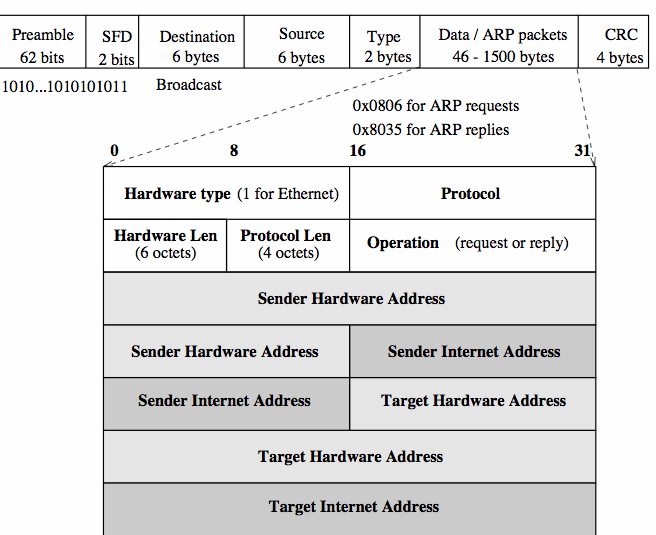 Unlike most protocols, ARP does not have a fixed format. Its design permits it to indicate how big its own fields will be, in this case that Ethernet addresses are 6 bytes (octets) long, and Internet addresses 4 bytes long. This permits ARP to be used with arbitrary network addressing schemes. When making a request, the sender (making the request) also supplies its own Ethernet/Internet address mapping. As all hosts on the Ethernet monitor the broadcast, they can update their mapping tables for future reference (ARP snooping).
CITS3002 Computer Networks, Lecture 7, The TCP/IP protocol suite, p13, 17th April 2024.
|