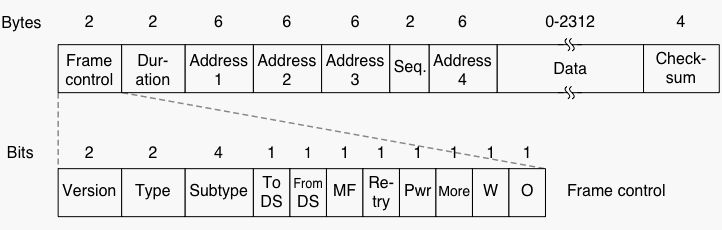
Access-Point Association
Although two mobile nodes can communicate directly,
the more usual approach is for all communication to be through fixed
access-points.
We say that a mobile node associates with a single access-point
if all of its communications are via that point,
and all such related nodes form a cell.
Communication between nodes in different cells requires two access-points
connected via a distribution system.
The mechanism employed by a mobile node to select an access-point is
termed active scanning:
- the mobile client node sends Probe frames,
- all access-points within range reply (if they have capacity)
with a Probe Response frame,
- the mobile node selects an access-point and sends
an Association Request frame, and
- the access-point responds with an Association Response frame.
An alternative is for an access-point to use passive scanning:
- the access-point periodically sends Beacon frames
advertising its existence and abilities (e.g. supported bandwidths),
- the mobile node may choose to switch to this new access-point using
Disassociation and Reassociation frames.
When a node selects a new access-point,
the new access-point is expected to inform the old access-point using the
distribution system.
CITS3002 Computer Networks, Lecture 4, Local Area Networks (LANs and WLANs), p22, 20th March 2024.
|


 CITS3002
CITS3002 help3002
help3002 CITS3002 schedule
CITS3002 schedule