

|
CITS3002 Computer Networks |
| ← prev | next → |  CITS3002
CITS3002 |
 help3002
help3002 |
 CITS3002 schedule
CITS3002 schedule |
|||
Phase Encoding of SignalsTo be able to detect collisions on LANs, we need to understand how digital signals are encoded on the physical medium. A digital signal is a sequence of discrete, discontinuous pulses, or signal elements. If all signal elements have the same (voltage) sign, they are termed unipolar. The modulation rate of a LAN is the number of signal elements (transitions) per second, or the baud rate. To correctly interpret a signal, the receiver must know the length (time) of each signal element and the expected voltage levels of the bits 0 and 1. The two simplest encoding schemes are the:
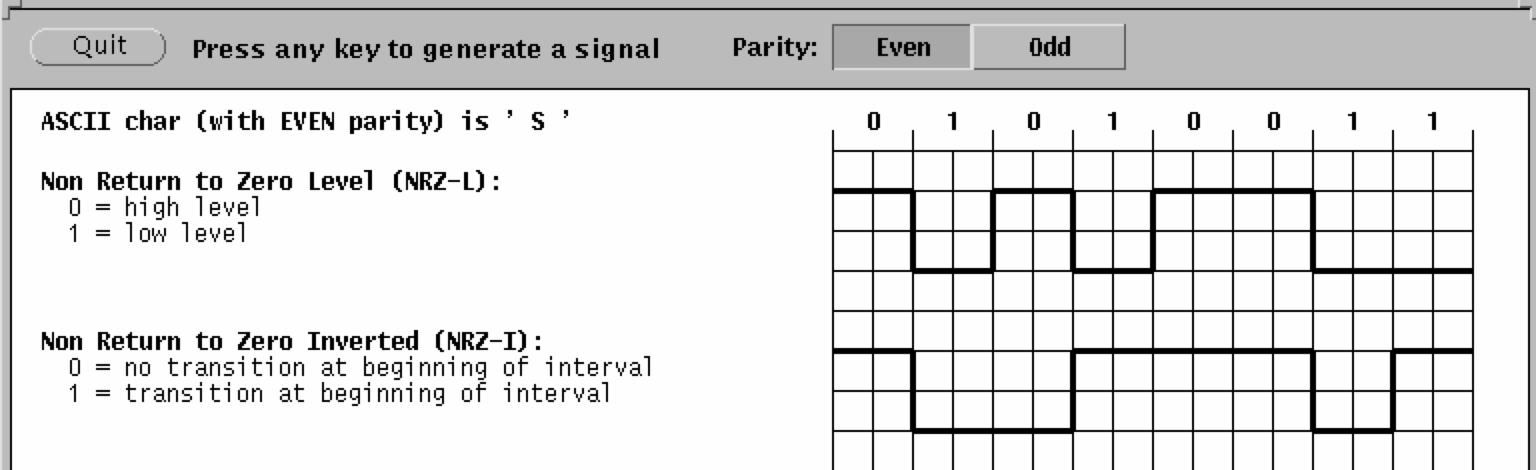
NRZ-I is an example of differential encoding in which the signal transition, rather than the signal level, indicates the value of each bit. See also: Sound of the dialup modem explained.
CITS3002 Computer Networks, Lecture 2, The Physical Layer, Errors detection and correction, p7, 6th March 2024.
|